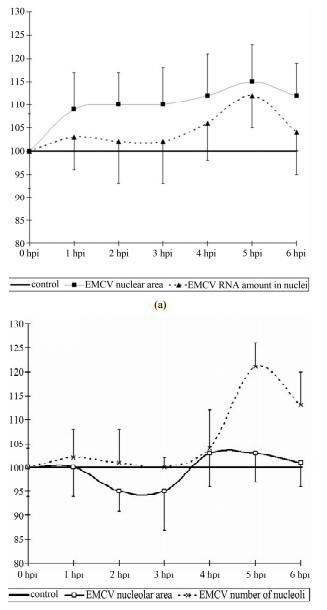
相关热词搜索:ABSTRACTBy the methods of quantitative cytophotometry, we have identified the changes in the nucleus and of some intranuclearcompartments in the early stages of infection with encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV). They can be characterized asearly 1 - 2 hours post infection (hpi) and temporary increase (duration about 1 hour) in the content of the acidic proteinsof the nucleolus, changing their decline to the control values. Then (after 1 - 2 hours) follows an increase in RNA contentof nucleoli to 4 hours post infection (the process takes about 2 hours). The increase in RNA content in nucleoli inapproximately the same time (slightly behind) with the activation of PML bodies (2 - 4 hpi). Then, the RNA content innucleoli decreased to the control values, while simultaneously decreasing activity of PML bodies (ranging from 5 - 6hpi). The early stages of infection EMCV is also characterized by the tendency to increase in the size of the nuclei ofinfected cells, and preserves at a later time. Then there is an increase in RNA content in the nucleus, roughly coincidingwith the increased content of RNA in the nucleoli.Keywords: EMCV; Acidic Proteins; RNA; Nucleolus; Nucleus1. IntroductionThe early stages of the replication of picornaviruses representan extreme interest, this is due to a relativelyshort period of time that the viruses which they will starttheir own replication, but also establish control over anumber of important cellular metabolic processes. Theresult of this phenomenon is a radical restructuring of theentire physiology of the infected cell. Part of the mechanismof this transformation has been clear for a long time,while others have only recently been clarified, but muchof it is still unknown.It is well known that picornaviruses are able to blockcap-dependent translation. Since picornaviral translationis cap-independent by virtue of the 5 IRES, many ofthese viruses have evolved potent mechanisms to inhibitcellular cap-dependent translation during infection,thereby thwarting detrimental antiviral responses. Theenteroviruses and aphthoviruses, for example, encodesecondary proteases at their 2A and L positions respectively,which target eIF4G [1]. Cardioviruses do nothave secondary proteases. Their L and 2A proteins haveessential host shut-off roles, but use non-proteolyticmechanisms to achieve them. The EMCV L (67 aa) contributesto the inhibition of cap-dependent translation bytriggering disruption of nucleocytoplasmic traffickingduring infection. For the disruption of cap-dependenttranslation of the host cells with EMCV, 2A protein isresponsible. As shown by [1], 2A NLS sequence is requiredfor virus shutoff of cap-dependent host proteinsynthesis.It has been shown that proteins of EMCV-the 2A, 3B(VPg), 3C (pro) and 3D (pol) can also be found withinthe nucleoli. The localization of these proteins occurs inthe first 2 - 4 hours following infection of cells [2,3].Therefore, it is important to study the influence of thepicornaviruses on the nuclear structure of infected cells.As it is well known, the replication of picornavirusesoccurs within the cytoplasm. However, at the earlieststages of viral infection many viral proteins are observedin the nucleus of affected cells. The research reported inthis paper was directed towards determining the DNA,RNA and acidic proteins (non histone) as well as PMLbodies in nuclei of EMCV infected cells. *Corresponding author.Copyright © 2013 SciRes. CellBio126 Z. A. KARALYAN ET AL.2. Materials and Methods2.1. CellsSK-N-MC human neuroblastoma cells were cultured inDulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) (Sigma)supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovineserum (FBS) at 37˚C in 5% CO2.2.2. VirusEMCV (Columbia-SK strain) was used at multiplicity ofinfection 105 TCD50/ml on SK-N-MC. Viral titers werecalculated by the method of Kärber. As a control the parallelconducted passages of noninfected cultures wereused.2.3. Image CytophotometryIn order to quantitative DNA analyze of the receiveddata, the cells preparations were fixed in 96% ethyl alcoholfor 30 minutes and painted in fresh Shiffs reactive,by Feulgen (hydrolyze 5N HCL 60 minutes at 22˚C). Thecontent of DNA in a nucleus and nucleolus was definedby computer-equipped microscope-photometer SMP 05(OPTON). The image cytophotometry of DNA was performedon 575 nm wave [4]. Unstimulated human lymphocyteswere used as diploid standards.For quantification of RNA was used gallocyaninchromalum stain. To obtain reproducible staining resultswith these large sections, the method of Einarson wasadapted to quantitative [5] and image analytical requirements.The image cytophotometry was performed on 610nm wave. In each case controls were evaluated as 100%.Fast green FCF staining (for acidic proteins) was usedin Deitch modification [6,7]. The image cytophotometrywas performed on 434 nm wave. In each case controlswere evaluated as 100%.2.4. Determination of the PMLCells grown on glass cover slips were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde/PBS(pH 7.5) for 5 minutes at room temperature,permeabilized in 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS for5 minutes at room temperature. PML protein was visualizedwith the monoclonal antibody. The determination ofthe PML was performed using monoclonal antibodies“PML PG-M3, Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc”-catalogueno. sc-966 FITC [8].2.5. StatisticsAll experiments were conducted in triplicate. The significanceof virus-induced changes was evaluated bytwo-tailed Student’s t-test. p values < 0.05 were consideredsignificant. SPSS version 15.0 software package(SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for statisticalanalyses.3. ResultsThe lytic EMCV infection was received by virus introductionon 48 h confluences of SK-N-MC culture. At 8hours post infection (hpi) the virus titer reached 3.0 lgTCD50/ml, at 12-4.0, at 24-4.5, at 24-72-6.5 (Figure 1).The time-course of a single cycle of EMCV reproductionin SK-N-MC cells take place about 8-12 h.The average content of the nucleolus to a nucleus doesnot change during the whole period of the experimentwith the exception of some minuscule increases of thecontent of nucleolus in a nucleus (2.5-control, 2.9-at 6hpi). The cytometry of the nucleolus values revealed thefollowing results: in the whole there are not definitechanges, but there may an emphasized tendency to increasethe given value up to the 6 hpi. The total area ofthe nucleoli increases almost by 35%, but due to largevariations in inpidual performance the difference is notreliable.Thus, when the infection with picornaviruses occursthe activation of the nucleolar values is detected. It has atemporary nature—first of all increases in the synthesisof the acidic proteins and after that an increase in thecontent of the RNA and the area of the nucleoli occurs.The quantitative indicators of DNA of the nucleus donot differ from the control values throughout the experiment,nor in the DNA content and neither in the distributionof DNA in ploidy classes.The size of the nucleus tends to increase in comparisonwith the control (p < 0.1), by 1 hpi and remain so untilthe end of the observation period (6 hpi) (Figure 2(a)).In addition the increase in the size of the nucleus is smalland varies from 8% - 11% from the baseline. It is importantto note that the increase in the size of the nuclei ofinfected cells is not accompanied by an increase in theRNA or acidic proteins of the nucleus. However, if thecontent of acidic proteins of the nucleus remained in arelatively stable index throughout the study, the RNA hasa tendency (t = 1.8, p < 0.1) increased by 5hpi, and coinFigure1. The titer of EMCV calculated on SK-B-MC cells.Copyright © 2013 SciRes. CellBioZ. A. KARALYAN ET AL. 127(a)(b)Figure 2. Dynamics of nuclear (a) and nucleolar (b) indicesunder the influence of EMCV infection. Data show percentageof control levels (average of 300 cells = 100%).cides with an increase in RNA in the nucleoli (Figure2(b)).As it follows from the Figure 3, in the early stages ofthe infection, there is an increase in the content (amount,concentration) of the nucleolar acidic proteins (with a 1-2 hpi) (t = 3.07, p < 0.05). The elevated level of acidicproteins has a short-period character, and after 1 hour (to3 hpi) its levels in the nucleolus does not differ from thebenchmarks. The increased levels of the acidic proteinsvary between 20% - 25% of the initial content.The RNA in the nucleoli of the infected and controlcells do not differ from each other, up to 4 hpi, when anFigure 3. Dynamics of nucleolar RNA and acidic proteinsunder the influence of EMCV infection. Data show percentageof control levels (average of 300 cells = 100%).increase in the RNA content in the nucleoli of infectedcells begins to be observed (Figure 3) (t = 2.17, p <0.05). The increase of the RNA in the nucleolus reaches30% - 35% in comparison with the control values. Theincrease of the RNA as long with the proteins has a shortperiod character and finishes after 5 hpi, decreasingdown to the levels of the control values (6 hpi).The intensity of the luminescence PML bodies, in thenuclei of the infected cells does not differ from the backgroundvalues in the range from 1 to 2 hpi. Then there isa sharp increase in the intensity of luminescence, whichindicates about the increased activity of PML bodies by 3hpi. Increased activity of PML bodies completely fadingaway to a 4 HPI, after which it does not differ from thecontrol values (Figure 4).We have identified the changes in the nucleus and ofsome intranuclear compartments in the early stages ofinfection EMCV.They can be characterized as early (1 - 2 hpi) andtemporary increase (duration about 1 hour) in the contentof the acidic proteins of the nucleolus, changing theirCopyright © 2013 SciRes. CellBio128 Z. A. KARALYAN ET AL.Figure 4. PML bodies in EMCV infected SK-N-MC cells. (A)PML bodies in control nuclei of SK-N-MC cells; (B) PMLbodies in infected nuclei of SK-N-MC cells (3 h.p.i). (C)PML bodies in infected nuclei of SK-N-MC cells (6 h.p.i.EMCV); (D) PML bodies in infected nuclei of SK-N-MCcells (9 h.p.i. EMCV) (×400).decline to the control values. Then (after 1 - 2 hours)follows an increase in RNA content of nucleoli to 4 hpi(the process takes about 2 hours). The increase in RNAcontent in nucleoli in approximately the same time(slightly behind) with the activation of PML bodies (2 - 4hpi). Then, the RNA content in nucleoli decreased to thecontrol values, while simultaneously decreasing activityof PML bodies (ranging from 5 - 6 hpi). The early stagesof infection EMCV is also characterized by the tendencyto increase in the size of the nuclei of infected cells, andpreserves at a later time. Then there is an increase inRNA content in the nucleus, roughly coinciding with theincreased content of RNA in the nucleoli.The total content of acidic proteins of the nucleus is arelatively stable index, changing a little both in the controland in the early stages of infection EMCV.4. DiscussionFor EMCV is found the involvement of the viral proteinsin the nuclear processes. Already in the early stages ofinfection (2 - 3 hpi) cardiovirus protein 2A, as well asproteins 3BVpg, 3Cpro, 3Dpolas a single precursor3BCD are located in the nucleoli of the cells, where thesynthesis of rRNA and ribosome assembly take place(Aminev et al., 2003a, Aminev et al., 2003b). The functionof the cardiovirus proteins in the nucleus of infectedcells have not been studied sufficiently. Protease 3Spropresumably responsible for the inhibition of synthesis ofcellular mRNA, whereas the work of RNA polymerases Iand III in cardiovirus infection are not inhibited [3]. Thefunction performed by the protein 2A of cardiovirus inthe nucleoli of the cells is not completely clear. Aminesand colleagues suggest that the protein 2A in the nucleoliembedded in the mature ribosomal subunits, resulting information of modified ribosomes engaged mainly in thecytoplasm of virus-specific protein synthesis [2]. Asshown by us, at this stage is a series of important structuraland functional changes in the nucleoli of infectedcells.With regard of the above said the increased content ofnucleolar acidic proteins in early stages of infectionEMCV could be explained by two reasons. The first isthe accumulation of the viral proteins and particularlyproteins 2A, 3BVpg, 3Cpro, 3Dpol and its predecessor3BCD. The second - the accumulation of nucleolar proteinswith enzymatic activity (discussed below).We haveidentified the data which allow us to assert that in theearly stages of infection (2 - 4 hpi) significant changesoccur in the nucleoli, coinciding with the localization ofviral proteins in them. These effects disappear in the laterstages of infection (6 hpi and later). This suggests ashort-term increase in the functional activity of the nucleolus[9] under the influence of infection EMCV. Inaddition to changes in the nucleoli, this process is accompaniedby an increase in the PML bodies. PMLbodies-small spherical domains are present in the nucleusof cells, they undergo morphological changes during thecell cycle. Their number is intensely variable, dependingon the physiological state of the cells, cell cycle stage inviral infections and so on. The PML bodies are destroyedduring some viral infections.Incubation of the cells with IFN induces the synthesisof the PML-protein and inhibits the multiplication of theviruses. These cells are destroyed during a viral infectionand for the replication of adenovirus DNA their destructtionis a necessary step that underlines the possible involvementof the corpuscles to provide antiviral activityof cells. Incubation of the cells with interferon inducesthe synthesis of PML-protein and inhibits proliferation ofsome viruses [10]. Upon infection of cells with the virusEMCV, it is shown a decrease in the number of the PMLbodies, under the influence of the viral 3C protease. Asthe mechanism of reduction of PML bodies, the authorsconsider a possible direct degradation of the PML bodies3C protease EMCV [11]. Thus, the sharp decrease inemission intensity of monoclonal antibodies to PML, to5.6 HPI, is explained by the influence of non-structuralviral proteins (3Cprotease), and aimed at suppressingIFN-mediated protection of the infected cell.We have also investigated the acidic proteins of chromatinand the nucleolus in a control experiment and underthe influence of the virus. Acidic proteins of thechromatin play an important role in the regulation of thegenetic activity. It was shown that in proliferating tissuescontain more acidic proteins than that of resting, andthese proteins are richer with euchromatin than with heterochromatin.The acidic proteins restore the DNA-dependentRNA synthesis, inhibited by histone, which enCopyright© 2013 SciRes. CellBioZ. A. KARALYAN ET AL. 129hance the transcription of chromatin in vitro and the activationof genes. Acidic proteins, in contrast to the histonesare tissue specific and bind to DNA only within thetissue from which they are allocated [12,13]. Taking intoaccount of our data it should be concluded that the activationof the transcription processes are in the range of 2- 4 HPI.Nucleolar acidic proteins—are a large group of proteinsassociated with the functional activity of the nucleolarproteins and the equivalent argentophilic proteins[14]. The most important argentophilic proteins: RNApolymerase I, transcription factor UBF, nucleolin (C-23),nucleophosmin (nyumatrin or B-23), etc. In contrast tothe widespread methods of silver protein, the quantitativecytochemical determination of acid proteins, allows usmore accurate identify variations in protein content, andhence the functional activity of the nucleolus [15-17].The role of these proteins in the replication of EMCV isunquestionable, since it is next to nucleophosmin (B-23)are localized EMCV proteins-the 2A, 3B (VPg), 3C (pro)and 3D (pol).It should be noted that the EMCV does not need nuclearstructures sensitive cells, as it is able to replicate ina cell-free medium containing the inpidual componentsof the damaged cells in the lysates [18]. Consequently,for successful replication the virus does not requiremodification of nucleolar apparatus.We can therefore conclude that any changes in the nucleoliare the result of the reaction of cells to viral infectionor virus modifies the activity of the nucleolus to thesuccessful suppression of cellular antiviral mechanisms.In our experiments, an elevated level of the acidicproteins in the nucleoli was preceded by the increasedcontent of RNA. The time gaps were approximately 1 - 2hours. RNA synthesis in the nucleoli is directly related tothe formation of the nucleoli. It should be noted that inthe temporal boundaries the biosynthesis of the nucleolifits into a space equivalent to about 1 hour. 7 - 10 minutesis the transcription of the rDNA, the synthesis of thesmall subunit of the ribosome—15 - 30 min, the synthesisof the large subunit of the ribosome—20 - 40 minutes[19]. It is possible that identified by us the time differencein the content of the acidic proteins and RNA inthe nucleolus is associated with the time of the biosynthesisof ribosomes.